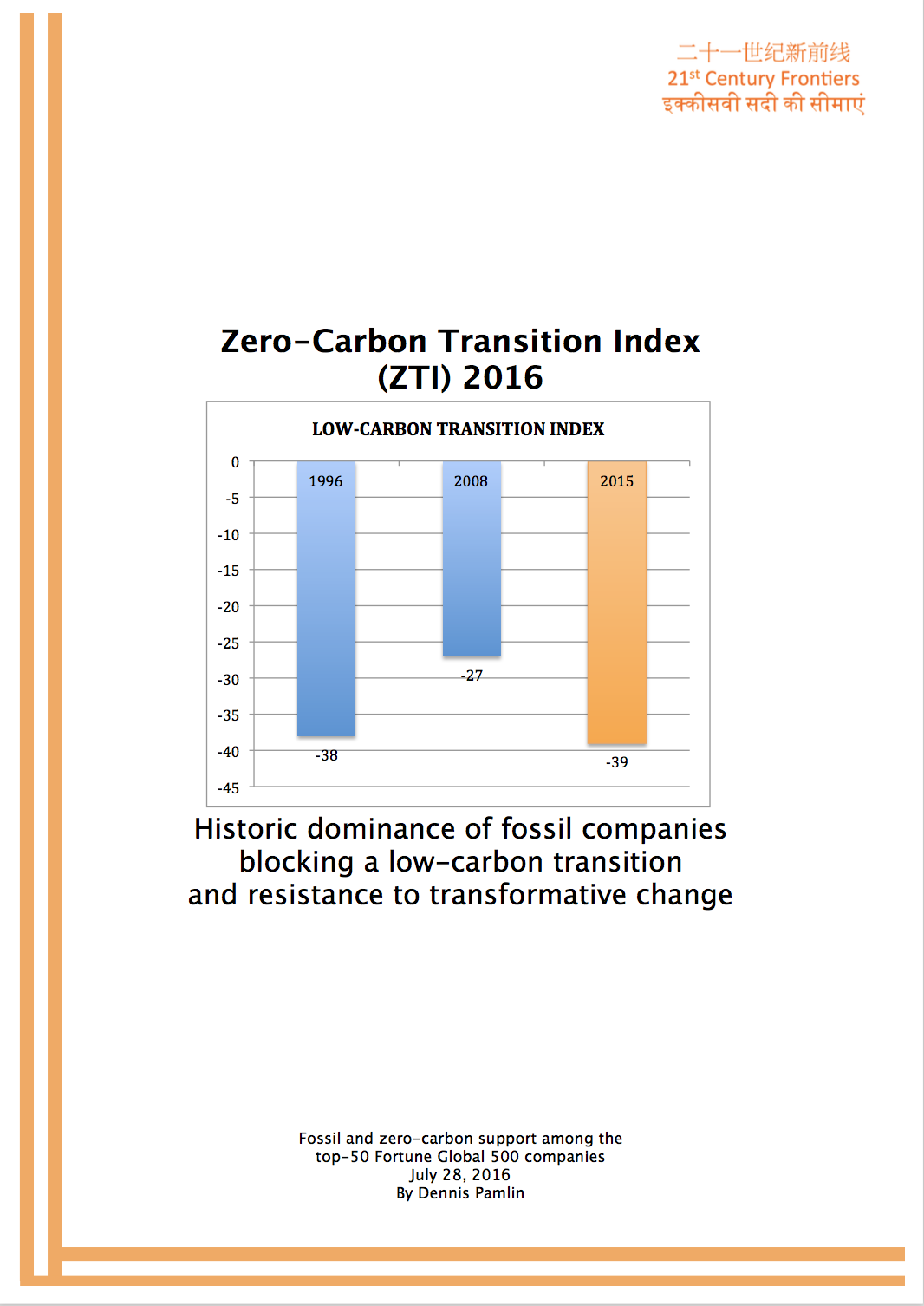
Role: author
Summary
To understand the current situation and the opportunities ahead, it is important to understand the different approaches companies have to take for a low carbon development and what kind of behaviour that different organisations and incentive structures promote.
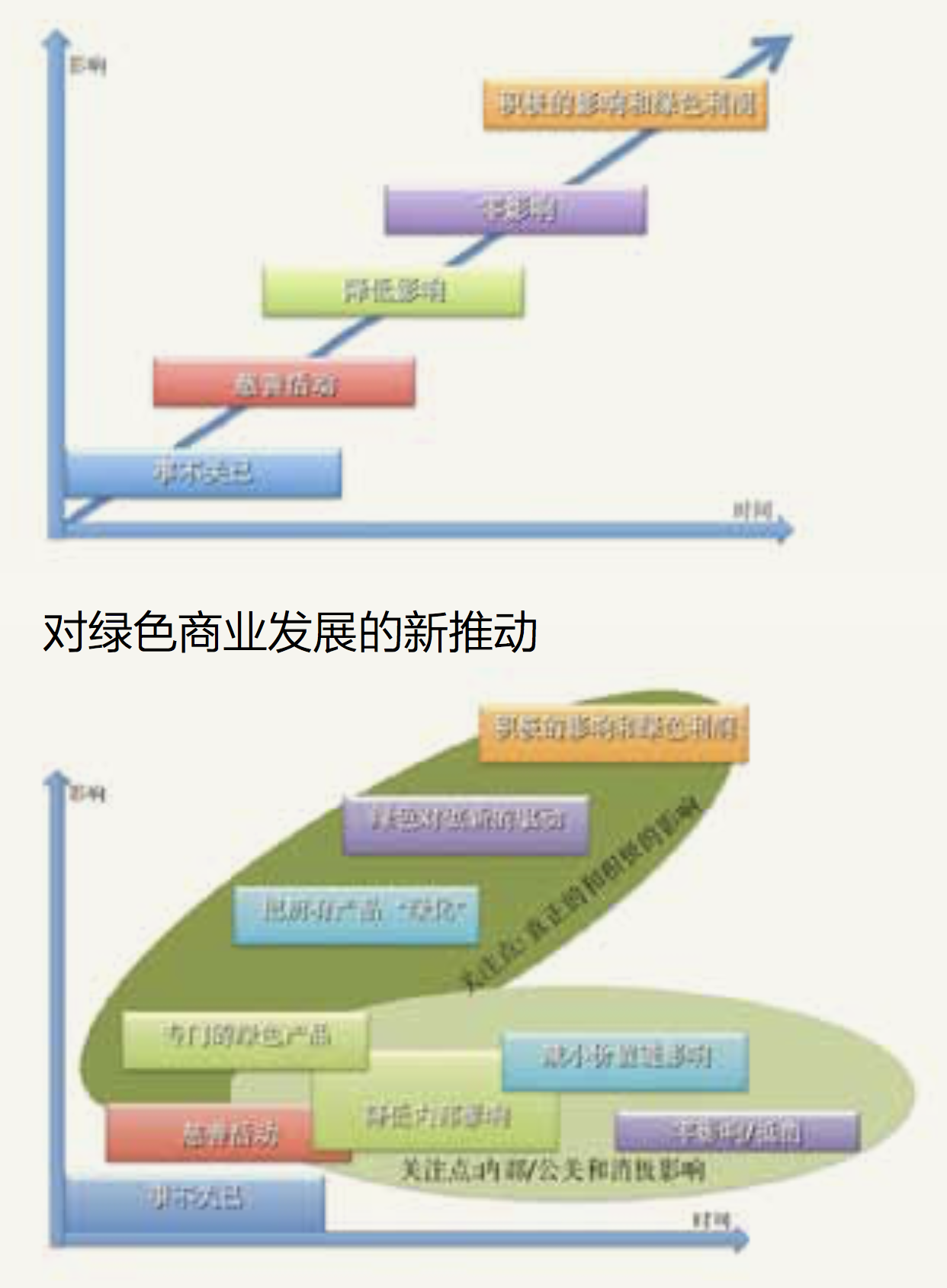
Four different levels of innovation can be identified, see Figure 4. The first level of low carbon innovation is when focus is on incremental improvements that reduce the company’s own problems. This is where most of the attention has been focused by policy makers, NGOs and businesses themselves. The reason for the focus is twofold: it is easily noticeable and understandable. When emissions are
discussed, people usually think about a coal power plant or just a chimney with smoke coming out. This focus makes sense for big polluters and only if incremental changes are needed.
The second level, which has got a lot of attention today, is incremental reductions through out the value chain, including all suppliers, starting from the extraction of material from nature and then also looking at the use-phase & end-use of the products. For most companies which are not the major emitters, it is in these parts where the majority of the emissions exist. Among IT companies, retailers, biotech companies and the manufacturing companies, up to 98% of the emissions cannot necessarily be associated with their own direct impact.
Still it is common for companies to aim for “climate neutral” and offset the emissions as they focus on level 1. This is a reason why offsetting might be one of the worst innovation killers today, keeping the companies on innovation level 1.
The third level is when the company acknowledge that the way they produce
things is not sustainable and instead of trying to improve unsustainable production methods, it develops solutions that become part of the solution. This can be a manufacturer of furniture that becomes a net producer of sustainable bio-energy, or a car manufacturer who builds so many wind power mills as it constructs its manufacturing plant & becomes a net producer to ensure that it puts more renewable energy on the grid than used.
The fourth level, and the most important level for the 21st century, is when the company starts to focus on what it is providing to society through its products and services. The question on this level is if the services the company provides are helping people getting a better life while helping to reduce emissions society2 then obviously the other levels are needed as well. But unless we get more companies to focus on how their core business is contributing to a low carbon economy, it will be impossible to reach the reductions needed.
Some people are afraid that focus on the core business, and solutions that company provides that can help reduce emissions in society, will distract them from the need to reduce their internal emissions. Looking at the companies that have begun to explore this area are almost leading in level 1-3 as well. Probably, because the companies that link low carbon development to their core business, requires a commitment from the CEO and the board. And if one wants to be the company that helps the customers towards a low carbon economy, it is not credible if the company has its own emissions. If anything is true, it is probably that many of the current initiatives that focus on internal emissions are distracting from effort on the higher innovation levels and not the other way around.
Download the full report